In today's world of advanced technology, we are constantly discovering new ways to understand and improve our health. One such technique is flow cytometry analysis, which allows us to examine the different types of white blood cells in our body. In this post, we will explore flow cytometry analysis in detail and how it can be used to identify and analyze Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells in the mouse mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs).
Flow Cytometry Analysis
Flow cytometry is a technique used to analyze individual cells, by measuring their physical and chemical properties. Cells are suspended in a solution, which passes through a tiny nozzle, and a laser beam is shone onto the cells as they pass through the nozzle. The laser beam reflects off the cells and is detected by sensors, which can analyze various properties of the cells.
One of the main uses of flow cytometry analysis is to examine the different types of white blood cells in our body. White blood cells are an essential component of our immune system, and they help to fight off infections and diseases. There are several different types of white blood cells, including T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cells
Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells are three different types of T cells, which play important roles in our immune system. Th1 cells produce cytokines that help to fight off intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria. Th2 cells produce cytokines that help to fight off extracellular pathogens, such as parasites and allergens. Th17 cells produce cytokines that help to fight off extracellular bacteria and fungi.
Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells are all important in maintaining immune homeostasis, and their levels can be affected by various factors, such as infections, diseases, and immunizations. Identifying and analyzing these cells is essential in understanding the immune response and developing effective treatments for diseases.
Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cells in the MLNs of Mice
The mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) are lymph nodes located in the mesentery of the small intestine. They are an essential component of the immune system and play an important role in filtering antigens from the gut.
A recent study used flow cytometry analysis to examine the levels of Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells in the MLNs of mice. The study found that the levels of Th1 cells were significantly higher in the MLNs of mice infected with a particular strain of bacteria, while the levels of Th2 cells were significantly higher in uninfected mice. The levels of Th17 cells were also higher in infected mice, although not significantly so.
Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy
Flow cytometry analysis involves the use of various gating strategies to identify and analyze different types of cells. One commonly used gating strategy for analyzing T cells involves gating on the CD3+ population, which helps to exclude other types of cells, such as B cells and natural killer cells.
Another gating strategy involves gating on the expression of various surface markers, such as CD4 and CD8, which are markers for helper and cytotoxic T cells, respectively. In the study discussed above, the gating strategy involved gating on the expression of CD4 and cytokines specific to Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells.
Conclusion
Flow cytometry analysis is a powerful tool that allows us to examine individual cells and understand the different types of white blood cells in our body. Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells play essential roles in our immune system, and identifying and analyzing these cells is a crucial step in understanding the immune response and developing effective treatments for diseases.
This recent study of Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells in the MLNs of mice provides valuable insights into the immune response to bacterial infections and illustrates the potential of flow cytometry analysis in immunology research. As technology continues to advance, flow cytometry analysis is likely to become an increasingly important tool in our efforts to improve our understanding of health and disease.
If you are searching about Flow cytometry gating strategy. Note: (A-F) Lymphocytes were gated by you've came to the right place. We have 7 Images about Flow cytometry gating strategy. Note: (A-F) Lymphocytes were gated by like Flow cytometry of sample from the lymph node of patient 3. The, Flow cytometry analysis of lymphoma cells in spleen, lymph node and and also Flow cytometry gating strategy. Note: (A-F) Lymphocytes were gated by. Read more:
Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy. Note: (A-F) Lymphocytes Were Gated By
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net cytometry gating lymphocytes gated cells cd45 doublets scatter
| Flow Cytometry Analysis Of Th1, Th2 And Th17 Cells In The MLNs Of
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net th2 th1 cytometry th17 mlns
Flow Cytometry Analysis Of Lymphoma Cells In Spleen, Lymph Node And
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net cytometry lymph node lymphoma spleen b220 results
Representative Flow Cytometry Plots Of Lymph Node Cells. The Cells Were
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net cytometry cells lymph plots acquired lymphocyte
Lymphatic System: Definition, Function, Diagram & Simple Explanation
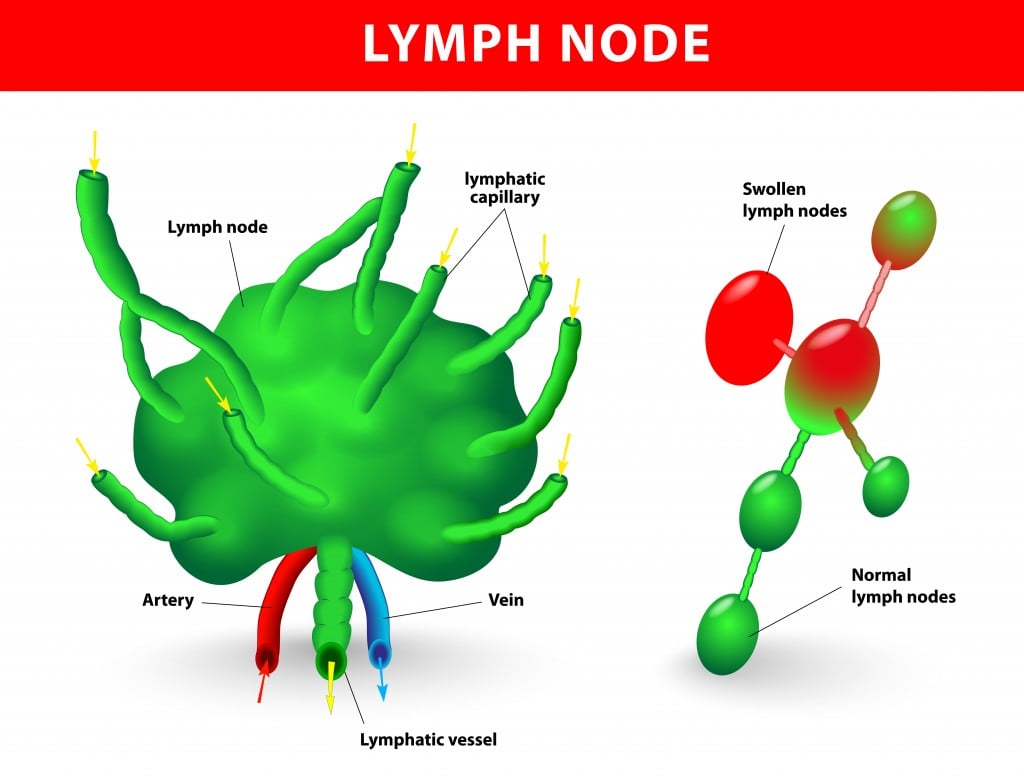 www.scienceabc.com
www.scienceabc.com lymph nodes lymphatic gland swollen linfonodo linfatico lymfeklier lymfeklieren designua linfonodi stockillustratie taping cervicale anatomie scienceabc
Flow Cytometry Of Sample From The Lymph Node Of Patient 3. The
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net lymph cytometry cd30 cd45 coexpression cd3 scatter hodgkin
Flow Cytometry Analysis Of Lymphoid Organs Of Gp130 F759/F759 Mice With
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net cytometry lymphoid gp130 f759 organs lymph arthritis node
Th2 th1 cytometry th17 mlns. Lymph nodes lymphatic gland swollen linfonodo linfatico lymfeklier lymfeklieren designua linfonodi stockillustratie taping cervicale anatomie scienceabc. Cytometry gating lymphocytes gated cells cd45 doublets scatter
Post a Comment for "Lymph Node Flow Cytometry Protocol"